NEW: Watch the executive summary
Most people resist change. As a consequence, the main job of an innovator will be to drive adoption, by convincing people and organizations to disrupt their routines.
Driving adoption means demonstrating to key stakeholders that disrupting the status quo is worth it and that adopting the innovation will bring significant perceived benefits.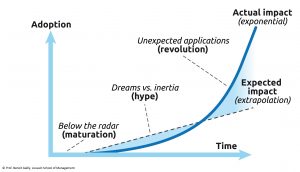
Driving adoption also means convincing key stakeholders that adopting new routines will be neither too difficult nor too risky, and that they and others can easily make it happen.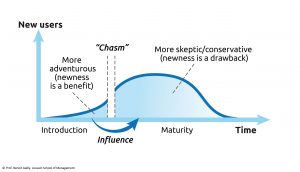
Bibliography
Resistance to change: disrupting routines
Keywords: human fear, inertia, job destruction, organizational routines, , path dependency, precautionary principle, resistance to change, responsible innovation, routines, technology assessment
- (Book) Callon, M. (2009). Acting in an uncertain world. MIT press.
- (Book) Godin, S. (2003). Purple cow: Transform your business by being remarkable. Penguin.
- (Book) Harremoës, P., Gee, D., MacGarvin, M., Stirling, A., Keys, J., Wynne, B., & Vaz, S. G. (2013). The precautionary principle in the 20th century: Late lessons from early warnings. Routledge.
- (Book) Juma, C. (2016). Innovation and its enemies: Why people resist new technologies. Oxford University Press.
- (Book) Kotter, J. P., & Rathgeber, H. (2006). Our iceberg is melting: Changing and succeeding under any conditions. Macmillan.
- (Book) Lewin, K. (2013). A Dynamic Theory of personality-Selected papers. Read Books Ltd.
- (Book) Perez, C. (2003). Technological revolutions and financial capital. Edward Elgar Publishing.
- (Book) Senge, P. M. (2014). The dance of change: The challenges to sustaining momentum in a learning organization. Crown Business
- (Video) Dean Kamen: To invent is to give (TED talk)
- (Video) Back to the Future
- (Video) How to Deal with Resistance to Change | Heather Stagl | TEDxGeorgiaStateU.
- (Article) Alexy, O., Henkel, J., & Wallin, M. W. (2013). From closed to open: Job role changes, individual predispositions, and the adoption of commercial open source software development. Research Policy, 42(8), 1325-1340.
- (Article) Bacq, S., & Aguilera, R. V. (2021). Stakeholder Governance for Responsible Innovation: A Theory of Value Creation, Appropriation, and Distribution. Journal of Management Studies, Forthcoming.
- (Article) Becker, M.C. (2004). Organizational routines: a review of the literature. Industrial and Corporate Change, 13(4), 643-678.
- (Article) Cohen, M. D., Burkhart, R., Dosi, G., Egidi, M., Marengo, L., Warglien, M., & Winter, S. (1996). Routines and other recurring action patterns of organizations: contemporary research issues. Industrial and Corporate Change, 5(3), 653-698.
- (Article) Dobusch, L., & Schüßler, E. (2012). Theorizing path dependence: a review of positive feedback mechanisms in technology markets, regional clusters, and organizations. Industrial and Corporate Change, 22(3), 617-647.
- (Article) Eggers, J. P., & Kaplan, S. (2013). Cognition and capabilities: A multi-level perspective. Academy of Management Annals, 7(1), 295-340.
- (Article) Feldman, M.S. (2000). Organizational Routines as a Source of Continuous Change. Organization Science, 11(6): 611-629
- (Article) Felin, T., & Foss, N. J. (2009). Organizational routines and capabilities: Historical drift and a course-correction toward microfoundations. Scandinavian Journal of Management, 25(2), 157-167.
- (Article) Ford, J. D., Ford, L. W., & D’Amelio, A. (2008). Resistance to change: The rest of the story. Academy of Management Review, 33(2), 362-377.
- (Article) Ford, J. D., & Ford, L. W. (2009). Decoding resistance to change. Harvard Business Review, 87(4), 99-103.
- (Article) Fosfuri, A., & Rønde, T. (2009). Leveraging resistance to change and the skunk works model of innovation. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 72(1), 274-289.
- (Article) Frambach, R. T., & Schillewaert, N. (2002). Organizational innovation adoption: A multi-level framework of determinants and opportunities for future research. Journal of Business Research, 55(2), 163-176.
- (Article) Geels, F. W., & Schot, J. (2007). Typology of sociotechnical transition pathways. Research Policy, 36(3), 399-417.
- (Article) Kotter, J. P. (1995). Leading change: Why transformation efforts fail. Harvard Business Review, Reprint 95204
- (Article) Kotter, J. P. (2012). Accelerate! Harvard Business Review, 90(11), 45-56
- (Article) Hannan, M. T., & Freeman, J. (1984). Structural inertia and organizational change. American Sociological Review, 149-164.
- (Article) Heidenreich, S., & Spieth, P. (2013). Why innovations fail—The case of passive and active innovation resistance. International Journal of Innovation Management, 17(05), 1350021.
- (Article) Hellström, T. (2003). Systemic innovation and risk: technology assessment and the challenge of responsible innovation. Technology in Society, 25(3), 369-384.
- (Article) Huy, Q. N. (2002). Emotional balancing of organizational continuity and radical change: The contribution of middle managers. Administrative Science Quarterly, 47(1), 31-69.
- (Article) Kleijnen, M., Lee, N., & Wetzels, M. (2009). An exploration of consumer resistance to innovation and its antecedents. Journal of Economic Psychology, 30(3), 344-357.
- (Article) Lapointe, L., & Rivard, S. (2007). A triple take on information system implementation. Organization Science, 18(1), 89-107.
- (Article) Le Bas, C., Mothe, C., & Nguyen-Thi, T. U. (2015). The differentiated impacts of organizational innovation practices on technological innovation persistence. European Journal of Innovation Management, 18(1), 110-127.
- (Article) Liebowitz, S. J., & Margolis, S. E. (1995). Path dependence, lock-in, and history. Journal of Law, Economics, & Organization, 205-226.
- (Article) Logue, D., & Grimes, M. (2022). Living up to the hype: How new ventures manage the resource and liability of future-oriented visions within the nascent market of impact investing. Academy of Management Journal, 65(3), 1055-1082.
- (Article) Mani, Z., & Chouk, I. (2018). Consumer resistance to innovation in services: challenges and barriers in the internet of things era. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 35(5), 780-807.
- (Article) Marcati, A., Guido, G., & Peluso, A. M. (2008). The role of SME entrepreneurs’ innovativeness and personality in the adoption of innovations. Research Policy, 37(9), 1579-1590.
- (Article) Marquis, C. (2003). The pressure of the past: Network imprinting in intercorporate communities. Administrative Science Quarterly, 48(4), 655-689.
- (Article) Pardo del Val, M., & Martínez Fuentes, C. (2003). Resistance to change: a literature review and empirical study. Management Decision, 41(2), 148-155.
- (Article) Pentland, B. T., & Feldman, M. S. (2005). Organizational routines as a unit of analysis. Industrial and Corporate Change, 14(5), 793-815.
- (Article) Schot, J., & Rip, A. (1997). The past and future of constructive technology assessment. Technological forecasting and social change, 54(2-3), 251-268.
- (Article) Sydow, J., Schreyögg, G., & Koch, J. (2009). Organizational path dependence: Opening the black box. Academy of Management Review, 34(4), 689-709.
- (Article) Szulanski, G. (1996). Exploring internal stickiness: Impediments to the transfer of best practice within the firm. Strategic Management Journal, 17(S2), 27-43.
- (Article) Van de Ven, A. H., & Poole, M. S. (1995). Explaining development and change in organizations. Academy of Management Review, 20(3), 510-540.
- (Article) Van de Ven, A. H., & Poole, M. S. (2005). Alternative approaches for studying organizational change. Organization Studies, 26(9), 1377-1404.
- (Article) Vergne, J. P., & Durand, R. (2010). The missing link between the theory and empirics of path dependence: conceptual clarification, testability issue, and methodological implications. Journal of Management Studies, 47(4), 736-759.
- (Article) Vuori, T., & Huy, Q. (2016). ‘Distributed Attention and Shared Emotions in the Innovation Process: How Nokia Lost the Smartphone Battle’. Administrative Science Quarterly, 61, 1-43.
- (Article) Walsh, J.P., & Ungson, G.R. (1991). Organizational memory. Academy of Management Review, 16(1), 57-91
Drivers of adoption: make it worth it
Keywords: adoption, bandwagon, diffusion, emergence, marketing of innovation, perceived benefits, social contagion, technology foresight
- (Book) Bijker, W. E., Hughes, T. P., & Pinch, T. J. (2012). The Social Construction of Technological Systems: New Directions in the Sociology and History of Technology.
- (Book) Cialdini, R.B. (2007) Influence: the Psychology of Persuasion
- (Book) Gladwell, M. (2006). The tipping point: How little things can make a big difference. Little, Brown.
- (Video) iDiots
- (Article) Abrahamson, E., & Rosenkopf, L. (1993). Institutional and competitive bandwagons: Using mathematical modeling as a tool to explore innovation diffusion. Academy of Management Review, 18(3), 487-517.
- (Article) Agarwal, R., & Bayus, B. L. (2002). The market evolution and sales takeoff of product innovations. Management Science, 48(8), 1024-1041.
- (Article) Aghion, P., Dechezleprêtre, A., Hemous, D., Martin, R., & Van Reenen, J. (2016). Carbon taxes, path dependency, and directed technical change: Evidence from the auto industry. Journal of Political Economy, 124(1), 1-51.
- (Article) Antonides, G., Bas Amesz, H., & Hulscher, I. C. (1999). Adoption of payment systems in ten countries-a case study of diffusion of innovations. European Journal of Marketing, 33(11/12), 1123-1135.
- (Article) Arts, J. W., Frambach, R. T., & Bijmolt, T. H. (2011). Generalizations on consumer innovation adoption: A meta-analysis on drivers of intention and behavior. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 28(2), 134-144.
- (Article) Bakker, S. (2010) The car industry and the blow-out of the hydrogen hype. Energy Policy, vol. 38, no. 11, pp. 6540-6544.
- (Article) Choi, J. N., Sung, S. Y., Lee, K., & Cho, D. S. (2011). Balancing cognition and emotion: Innovation implementation as a function of cognitive appraisal and emotional reactions toward innovation. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 32(1), 107-124.
- (Article) Cialdini, R.B., & Goldstein, N.J. (2004) Social influence: Compliance and conformity. Annu. Rev. Psychol., 55, 591-621.
- (Article) Eerkens, Jelmer W., and Carl P. Lipo. “A tale of two technologies: Prehistoric diffusion of pottery innovations among hunter-gatherers.” Journal of Anthropological Archaeology 35 (2014): 23-31.
- (Article) Geroski, P. A. (2000). Models of technology diffusion. Research Policy, 29(4-5), 603-625.
- (Article) Gollier, C. (2001). “Should we beware of the precautionary principle?” Economic Policy, 33, 303-327.
- (Article) Iyengar, R., Van den Bulte, C., & Valente, T. W. (2011). Opinion leadership and social contagion in new product diffusion. Marketing science, 30(2), 195-212.
- (Article) Jeyaraj, A., Rottman, J. W., & Lacity, M. C. (2006). A review of the predictors, linkages, and biases in IT innovation adoption research. Journal of Information Technology, 21(1), 1-23.
- (Article) Nelson, R. R., Peterhansl, A., & Sampat, B. (2004). Why and how innovations get adopted: a tale of four models. Industrial and Corporate Change, 13(5), 679-699.
- (Article) Saloner, G., & Shepard, A. (1992). Adoption of technologies with network effects: an empirical examination of the adoption of automated teller machines (No. w4048). NBER
- (Article) Seligman, L. (2006). Sensemaking throughout adoption and the innovation-decision process. European Journal of Innovation Management, 9(1), 108-120.
- (Article) Stock, R., von Hippel, E., & Gillert, N. (2016). ‘Impacts of personality traits on consumer innovation success’. Research Policy, 45, 757-769.
- (Article) Tornatzky, L. G., & Klein, K. J. (1982). Innovation characteristics and innovation adoption-implementation: A meta-analysis of findings. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, (1), 28-45.
- (Article) Van den Bulte, C., & Joshi, Y. V. (2007). New product diffusion with influentials and imitators. Marketing science, 26(3), 400-421.
- (Article) Venkatesh, V., & Davis, F. D. (2000). A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: Four longitudinal field studies. Management Science, 46(2), 186-204.
- (Article) Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., & Davis, F. D. (2003). User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS quarterly, 425-478
- (Article) Venkatesh, V., Thong, J. Y., & Xu, X. (2012). Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. MIS quarterly, 36(1), 157-178.
Drivers of adoption: make it easy
Keywords: adoption hurdles, adoption engineering, compatibility, complexity, cultural ambience, influencer, observability, product lifecycle, public sector innovation, skeuomorphism, standardization, switching costs, triability
- (Book) Abrahamson, E. (2004). Change without pain: How managers can overcome initiative overload, organizational chaos, and employee burnout. Harvard Business Press.
- (Book) Eagleman, D., & Brandt, A. (2017). The Runaway Species: How human creativity remakes the world. Catapult.
- (Book) Fagerberg, J. (2005) The Oxford Handbook of Innovation, Oxford University Press.
- (Book) Norman, D. A. (2013). The design of everyday things: Revised and expanded edition. Basic books.
- (Book) Rogers, E. M. (2010). Diffusion of innovations. Simon and Schuster.
- (Book) Thaler, R. and Sunstein, R. (2012) Nudge
- (Book) Dawkins, R. (2016). The selfish gene. Oxford university press.
- (Video) The Zinnovants, “Convince”
- (Video) The diffusion of innovation theory (Aiman Pht)
- (Article) Adner, R. (2006). Match your innovation strategy to your innovation ecosystem. Harvard Business Review, 84(4), 98.
- (Article) Adner, R., & Kapoor, R. (2016). Right Tech, Wrong Time. Harvard Business Review, 94(11), 60-67.
- (Article) Albury, D. (2005). Fostering innovation in public services. Public Money and Management, 25(1), 51-56.
- (Article) Allen, R. H., & Sriram, R. D. (2000). The role of standards in innovation. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 64(2-3), 171-181.
- (Article) Bass, F.M. (2004). Comments on “a new product growth for model consumer durables the bass model”. Management Science, 50(12_supplement), 1833-1840.
- (Article) Bessant, J. (2005). Enabling continuous and discontinuous innovation: Learning from the private sector. Public Money and Management, 25(1), 35-42.
- (Article) Chakravorti, B. (2004). The new rules for bringing innovations to market. Harvard Business Review, 82(3), 58-67.
- (Article) Choi, J. N., & Chang, J. Y. (2009). Innovation implementation in the public sector: An integration of institutional and collective dynamics. Journal of Applied Psychology, 94(1), 245.
- (Article) Chiesa, V., & Frattini, F. (2011). Commercializing technological innovation: Learning from failures in high‐tech markets. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 28(4), 437-454.
- (Article) Coeurderoy, R., Guilmot, N., & Vas, A. (2014). Explaining factors affecting technological change adoption: A survival analysis of an information system implementation. Management Decision, 52(6), 1082-1100.
- (Article) Damanpour, F., & Schneider, M. (2008). Characteristics of innovation and innovation adoption in public organizations: Assessing the role of managers. Journal of Public Administration Research and Theory, 19(3), 495-522.
- (Article) De Vries, H., Bekkers, V., & Tummers, L. (2016). Innovation in the public sector: A systematic review and future research agenda. Public Administration, 94(1), 146-166.
- (Article) Frambach, R. T., Barkema, H. G., Nooteboom, B., & Wedel, M. (1998). Adoption of a service innovation in the business market: an empirical test of supply-side variables. Journal of Business Research, 41(2), 161-174.
- (Article) Goldenberg, J., Han, S., Lehmann, D. R., & Hong, J. W. (2009). The role of hubs in the adoption process. Journal of Marketing, 73(2), 1-13.
- (Article) Greenhalgh, T., Robert, G., Macfarlane, F., Bate, P., & Kyriakidou, O. (2004). ‘Diffusion of Innovations in Service Organizations: Systematic Review and Recommendations’. The Milbank Quarterly, 82, 581-629.
- (Article) Greenwood, R., Suddaby, R., & Hinings, C. R. (2002). Theorizing change: The role of professional associations in the transformation of institutionalized fields. Academy of Management Journal, 45(1), 58-80.
- (Article) Griliches, Z. (1957). Hybrid corn: An exploration in the economics of technological change. Econometrica, Journal of the Econometric Society, 501-522.
- (Article) Hameed, M. A., & Counsell, S. (2014). Establishing relationships between innovation characteristics and IT innovation adoption in organisations: A meta-analysis approach. International Journal of Innovation Management, 18(01), 1450007.
- (Article) Hard M. & Knie A. (2001) The cultural dimension of technology management: Lessons from the history of the Automobile. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management Vol. 13(1);
- (Article) Hartley, J. (2005). Innovation in governance and public services: Past and present. Public Money and Management, 25(1), 27-34.
- (Article) Leonard-Barton, D., & Sinha, D. K. (2017). Developer-user interaction and user satisfaction in internal technology transfer. Academy of Management Journal.
- (Article) Lounsbury, M. (2007). A tale of two cities: Competing logics and practice variation in the professionalizing of mutual funds. Academy of Management Journal, 50(2), 289-307.
- (Article) Mahajan, V., Muller, E., & Bass, F. M. (1990). New product diffusion models in marketing: A review and directions for research. Journal of Marketing, 54(1), 1-26.
- (Article) Micheli, P., Schoeman, M., Baxter, D., & Goffin, K. (2012). New business models for public-sector innovation: Successful technological innovation for government. Research-Technology Management, 55(5), 51-57.
- (Article) Mustonen‐Ollila, E., & Lyytinen, K. (2003). Why organizations adopt information system process innovations: a longitudinal study using Diffusion of Innovation theory. Information Systems Journal, 13(3), 275-297.
- (Article) Reinders, M. J., Frambach, R. T., & Schoormans, J. P. (2010). Using product bundling to facilitate the adoption process of radical innovations. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 27(7), 1127-1140.
- (Article) Tucker, C. (2008). Identifying formal and informal influence in technology adoption with network externalities. Management Science, 54(12), 2024-2038.
- (Article) van Oorschot, J. A., Hofman, E., & Halman, J. I. (2018). A bibliometric review of the innovation adoption literature. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 134, 1-21.
- (Article) Wisdom, J. P., Chor, K. H. B., Hoagwood, K. E., & Horwitz, S. M. (2014). Innovation adoption: a review of theories and constructs. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research, 41(4), 480-502.
(c) Prof. Benoit Gailly, Louvain School of Management


